Exploring the World of Tinted Glass in Modern Design
Tinted glass stands as a popular architectural and automotive glass variant, appreciated for its aesthetic appeal, solar control properties, and privacy enhancements. This specialized glass undergoes a unique manufacturing process to imbue it with color, offering various hues and degrees of opacity. It finds multifaceted uses across residential, commercial, and automotive applications, providing an amalgamation of functionality and style.
Types of Tinted Glass:
Heat-Absorbing Tinted Glass: This type of tinted glass is designed to reduce solar heat gain by absorbing a portion of the sun’s energy. It assists in maintaining cooler interior temperatures, reducing reliance on air conditioning systems, and enhancing energy efficiency.
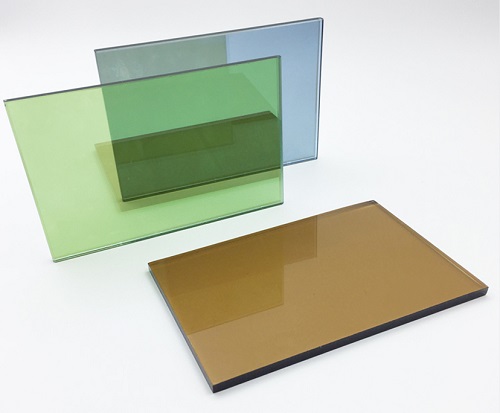

Reflective Tinted Glass: Reflective tinted glass, also known as solar control glass, features a reflective surface that reflects a significant portion of solar radiation. It prevents heat buildup within interiors while offering privacy by acting as a one-way mirror.
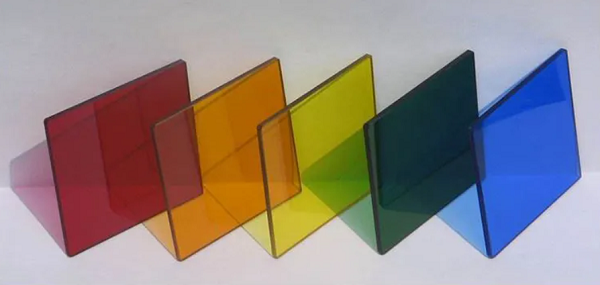
Colored Tinted Glass: Colored tinted glass introduces various hues and shades, providing decorative and aesthetic enhancements. It is available in a spectrum of colors, offering design versatility and customization options.
Processing of Tinted Glass:
Tinted glass undergoes a process known as tinting or coloring during manufacturing to achieve the desired color and opacity:
Additives: During the glass manufacturing process, specific additives or compounds, such as metal oxides like iron, selenium, or cobalt, are introduced to the glass melt. These additives influence the glass’s coloration, giving it the desired tint.

Annealing and Cooling: Once the glass is formed, it undergoes an annealing process to relieve internal stresses and ensure structural integrity. It is then gradually cooled to room temperature in a controlled environment.
Quality Control: Throughout the manufacturing process, stringent quality checks are conducted to ensure uniformity, color accuracy, and durability of the tinted glass.
Uses of Tinted Glass:
Tinted glass finds a wide array of applications across diverse industries:
Architectural Applications: Tinted glass is utilized in building facades, windows, doors, and skylights. It offers solar control, reduces glare, and enhances the building’s aesthetics.
Automotive Industry: Tinted glass is extensively used in car windows, windshields, and sunroofs to reduce heat and glare, improve privacy, and enhance the vehicle’s appearance.
Interior Design: It is employed in interior partitions, decorative panels, and furniture elements to add color, privacy, and style to spaces.

Electronics: Tinted glass is used in electronic devices, such as screens and displays, to reduce glare and improve readability.
Tinted glass, with its versatility, aesthetic appeal, and functional properties, continues to be a preferred choice in various applications, offering a harmonious blend of style, solar control, privacy, and energy efficiency. Its ability to cater to diverse design requirements while providing practical benefits makes it an integral component in modern architecture and automotive design.





