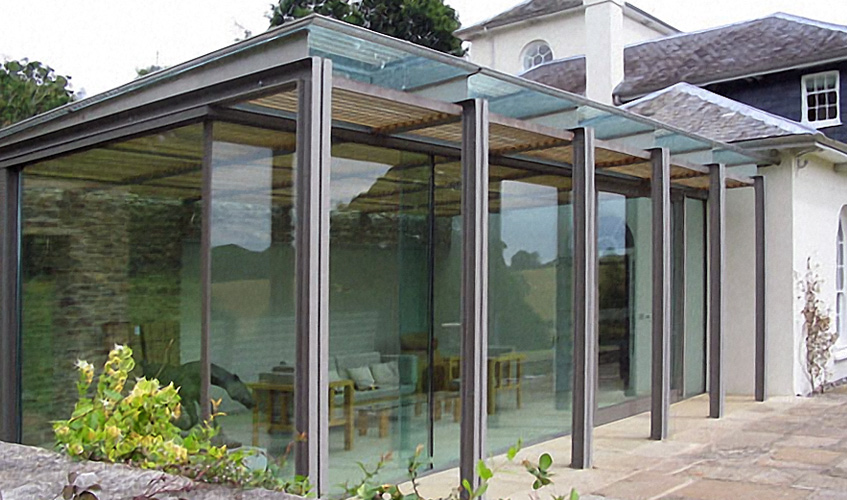

Everything to Know About Laminated Glass, Uses, Applications
Laminated glass is a specialized type of safety glass composed of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer material, typically a polymer such as polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA). This unique construction makes laminated glass highly resilient to impact, offering enhanced safety and security in various applications. In this blog post, we will delve into the characteristics, types, uses, and benefits of laminated glass, shedding light on its importance in modern architecture and design.
Characteristics of Laminated Glass:
Safety: One of the primary characteristics of laminated glass is its safety properties. In the event of breakage, the interlayer holds the glass fragments together, preventing them from scattering and reducing the risk of injury from sharp edges and flying debris.
Security: Laminated glass provides increased security compared to traditional annealed glass, as it is more difficult to penetrate or break through. This makes it an ideal choice for applications requiring protection against forced entry or vandalism.
Sound Insulation: The layered construction of laminated glass helps dampen sound transmission, making it effective for noise reduction in urban environments, transportation hubs, and commercial buildings.

UV Protection: Some types of interlayer materials used in laminated glass have UV-blocking properties, providing protection against harmful ultraviolet rays. This helps prevent fading and damage to interior furnishings, artwork, and occupants.
Durability: Laminated glass is more durable and impact-resistant than monolithic glass, making it suitable for applications requiring long-term performance and reliability.
Versatility: Laminated glass can be customized with various combinations of glass types, thicknesses, and interlayer materials to meet specific design requirements and performance criteria.
Aesthetic Options: Laminated glass is available in a range of options, including clear, tinted, and decorative interlayers, allowing for customization to achieve desired aesthetics while maintaining safety and security.
Types of Laminated Glass:
Clear Laminated Glass: Clear laminated glass consists of two or more layers of clear glass bonded together with a transparent interlayer. It offers unobstructed views and maximum light transmission, making it suitable for applications such as windows, doors, and skylights.
Tinted Laminated Glass: Tinted laminated glass incorporates colored interlayers to achieve specific aesthetic effects or provide solar control properties. Tinted glass can help reduce glare, control heat gain, and enhance privacy in architectural applications.
Low-E Laminated Glass: Low-emissivity (low-E) laminated glass features a coating applied to one or more glass surfaces to reduce heat transfer and improve energy efficiency. Low-E glass helps retain heat in winter and block solar heat gain in summer, resulting in lower heating and cooling costs.
Decorative Laminated Glass: Decorative laminated glass includes patterned, frosted, or digitally printed interlayers that add visual interest and design flair to architectural elements. Decorative glass is often used in partitions, balustrades, and interior doors to create striking visual effects.
Safety and Security Laminated Glass: Safety and security laminated glass is specifically engineered to withstand high-impact forces and resist penetration from blunt objects or projectiles. It is commonly used in applications requiring protection against burglary, vandalism, and natural disasters.
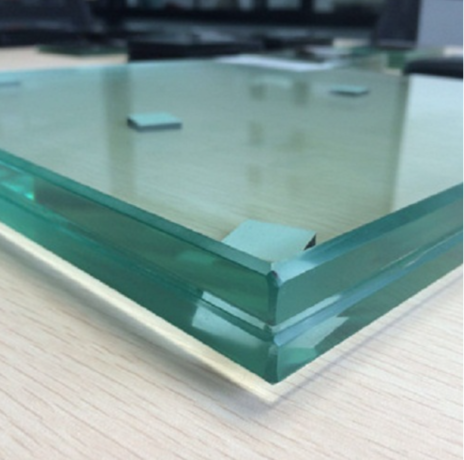
Uses of Laminated Glass:
Architectural Glazing: Laminated glass is widely used in architectural glazing applications such as windows, doors, curtain walls, and glass facades. Its safety, security, and sound insulation properties make it an ideal choice for building exteriors.
Automotive Glass: Laminated glass is used in automotive windshields to provide occupant safety and protection in the event of a collision. The laminated construction prevents the windshield from shattering upon impact, reducing the risk of injury to vehicle occupants.
Safety Barriers: Laminated glass is employed in safety barriers, balustrades, and guardrails to provide fall protection and prevent accidents in elevated areas such as balconies, staircases, and terraces.
Hurricane and Storm Protection: In regions prone to hurricanes and severe weather events, laminated glass is used to protect buildings from windborne debris, impact damage, and water infiltration. Hurricane-resistant laminated glass helps safeguard properties and occupants during extreme weather conditions.
Bulletproof and Blast-Resistant Glass: Laminated glass can be engineered to withstand ballistic threats and explosive forces, making it suitable for applications requiring high levels of security, such as government buildings, banks, and embassies.
Benefits of Laminated Glass:
Safety and Security: Laminated glass enhances occupant safety and security by minimizing the risk of injury from broken glass and providing protection against forced entry and vandalism.
Sound Insulation: The layered construction of laminated glass helps reduce noise transmission, creating quieter and more comfortable indoor environments.
UV Protection: Laminated glass with UV-blocking interlayers helps protect interior furnishings, artwork, and occupants from harmful ultraviolet radiation, prolonging the lifespan of materials and reducing fading.
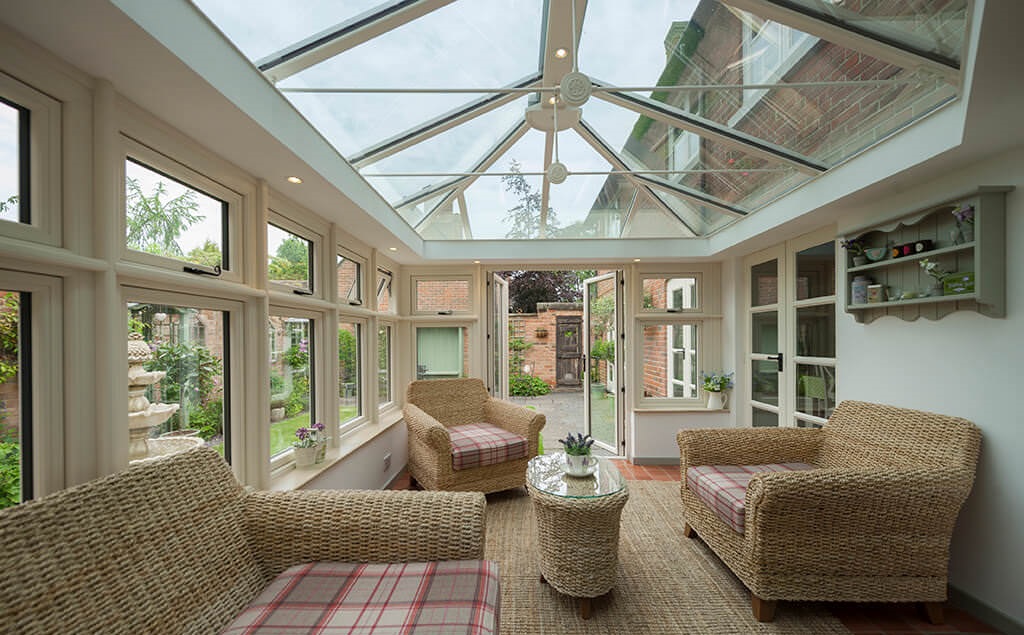

Design Flexibility: Laminated glass offers designers and architects flexibility in achieving design goals while meeting safety and performance requirements. It can be customized with various interlayer materials, thicknesses, and aesthetic options to achieve desired aesthetics and functionality.
Energy Efficiency: Low-E laminated glass improves energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer and minimizing heating and cooling loads. It helps maintain comfortable indoor temperatures year-round and reduces reliance on artificial heating and cooling systems.
Laminated glass is a versatile and innovative building material that offers a unique combination of safety, security, and aesthetic versatility. From architectural glazing to automotive applications, laminated glass plays a vital role in enhancing occupant safety, improving energy efficiency, and adding visual interest to architectural and design projects. As technology continues to advance and sustainability becomes increasingly important, laminated glass will continue to evolve, offering new possibilities for creating safe, sustainable, and visually stunning built environments.
Related Posts:
Exploring Reflective Glass: Uses, Characteristics, and Fascinating Facts





